Binary & Digital Options vs Forex & CFD
If you are new to trading then you may be slightly confused as to how Forex and CFD differ from Binary Options. These instruments are almost intertwined. One cannot really successfully trade the one without a basic understanding of the others.
How can one be expected to trade Binary Options on Forex pairs profitably without knowing how to trade Forex in general? This is why many new traders to the more exotic instruments tend to lose money.
As with anything in life, one has to learn to walk before they can run. In this post, we will go through the key characteristics of the assets and how they are similar / different.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading is the most easy to understand example of trading. Essentially, the trader is buying and selling foreign currency. For example, they would be buying Euros with Dollars and this would be trading EURUSD.
This is in contrast to the trading of shares and commodities. Although these assets are indeed interesting in their own right, they are by no means as vast as the Forex market.
The Foreign Exchanged (FX) market is also the largest market on the planet with trillions of dollars changing hands every day. However, the majority of these transactions are completed by large financial institutions and multinationals.
Trading Forex is also one of the oldest ways in which retail traders have been investing online. Given the size and liquidity of the market, people have found trading currencies to be one of the most interesting.
When online forex trading was first released back in the early days of the internet, traders could only buy and sell forex using the currency that they hold in their accounts.
This means that if the account was a US based account and denominated in USD, the trader would only be able to trade US dollar crosses.
That was until other derivative instruments were offered to retail traders. Derivatives are essentially assets where their value is derived from the price of the underlying asset.
Two of the most common derivative instruments in the market today are binary options and CFDs.
What is a CFD?

As mentioned, a CFD (Contract for Difference) is a derivative instrument on another asset. This asset could be anything from Forex to Equities and Commodities.
It is essentially a contract that settles the profit and loss every day based on the difference between the price at the start of the day and the price at the end of the day.
The trader will never actually own the underlying asset but will have taken a “bet” on the direction of the asset. This is a great solution for those traders that want to trade forex pairs that are not denominated in their account currency.
For example, a trader who was based in the USA could just as easily trade AUD/NZD as he could EUR/USD. The only thing that will be calculated in USD will be the trader’s profit.
Another reason that a CFD is an interesting investing instrument is because it means that the trader can enter a trade where the trade size is much larger than the amount of funds that they have in the account.
The term for this is “trading on margin” or leverage. This is what instruments such as CFDs and spread betting are well known for.
Indeed, because traders are able to take very large positions in assets that they do not hold, they can make a much larger return for a certain percentage move.
Of course, there is also a much larger risk on the downside for the trader. If the asset moves against the trader then they are likely to lose a much larger percentage than they staked. This is when they get a margin call.
This is why CFDs and other instruments with high degrees of leverage are not recommended for traders with no experience of the market. Unless there are adequate stops in place and the trader uses proper risk management strategies they may lose all of their investments.
Hence, there were some online retail investors who wanted to make use of some instruments that had a different risk profile to CFDs. This was when options and binary options started to enter the market.
What is an Option (Digital Contracts) ?
These are a relatively new investment instrument that has been made available on the market. They are a combination of a binary Option and a CFD. They are essentially contracts where the trader can either enter a PUT or a CALL.
Options are instruments that allow the holder the right but not the obligation to buy or sell some asset at a predetermined price and at a predetermined time.
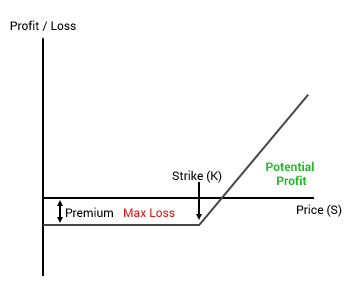
Given that options confer a right by the trader to buy / sell the asset, they have an asymmetric payoff. What this means is that the gains / losses on the option are not equal on either side. This is explained pretty well in the image to the right.
This is the payoff of a traditional CALL option. As you can see the potential gains if the price passes the strike is indeed positive and is uncapped whereas the maximum loss is limited to the option premium.
The trader could make small gains on the instruments by entering contracts which are close to in the money. They could also make large gains on those contracts that are far out of the money.
This could work well for the trader that aims to make a profit from a large movement in the price on events such as price action moves on release of important economic news. The trader could enter contracts that are deep out of the money.
However, traditional options can still be complicated to understand and are usually only traded by investors who know how to trade “volatility” in the industry. They are best able to manage the risk.
What is a Binary Option?
Binary Options are a relatively well known exotic option on Wall Street and have been used for a number of years. It was only in about 2008 that they were being offered on the retail market to average investors.
They were considered as more exotic and were used for speculation on events with binary outcomes.
A binary option is in essence a variant of a traditional financial option. It has the same characteristics, namely a strike, expiry time and price. The difference between a binary option and a CFD is that a binary option has a binary payoff. The trader can either get 1 (or 100) or 0.
This makes Binary Options a relatively straightforward type of instrument as the trader knows from the outset how much they are likely to gain or lose on the investment. It gives a certain degree of certainty for the investment which allows a range of binary option strategies to be employed
Technically, they differ from traditional options when it comes to their payoff. The trader does not have an unlimited upside but has the chance to gain a particular amount that is usually 100. We have previously explained binary options in more detail.
Yet, from the perspective of the retail trader, binary options create an opportunity for a more simple type of trading. The trader knows exactly how much they are likely to gain or lose when they place a trade.
In all practicality, the trader is taking a view on whether the asset will go up or down in price over the trade period. If the trader thinks that the price is going to go up then they will enter a CALL option. If they think that it will go down then they enter PUT option.
At the end of the trade, depending on where the price of the asset is in relation to the strike price, the trader will either get the positive pay-out that they were hoping for or they will lose the investment premium.
Given this relatively simple nature, a number of new traders have traded binary options with a cavalier attitude and have not used any trading strategies when placing the trades.
A trader should always have a binary options strategy in place before they decide to start trading. This should not be done in isolation and should also take account of strategies relating to the underlying asset.
How do they Differ?
Binary Options and CFDs are merely derivatives of traditional forex assets. They are also derivatives of other assets such as commodities, equities and crypto currency.
For example, when a trader is buying a CALL option on EURUSD they are in effect entering a long position on the currency pair. The opposite can be said of a PUT option and shorting the asset.
The only way these instruments will in fact differ is in the range of assets that you can trade and the amount of risk that you can take.
There are also a range of other more exotic binary option types that are offered by some brokers including one touch options, tunnel options and turbo options.
These just present the trader with more opportunities to profit from unique movements in the price of the asset. If you are a trader who knows his / her strategies, they can be quite interesting.
Which One Should I Trade?
This is usually one of the most important questions that the trader should answer before they decide to invest any money. Indeed, some of these instruments appeal to different personalities.
What is however crucial is that the trader has an understanding of how to trade the underlying asset (forex in this case) before they embark on trading any of their derivatives.
For example, the trader cannot be expected to make money trading binary options if they don’t have an idea of how the underlying asset will move. This will severely impact their profitability.
Therefore, the trader should at least spend a bit of time understanding how traditional forex is traded and how they are expected to profit from it.
Then, once they have a reasonable understanding of forex, they should decide which type of derivative instrument they would like to trade.
CFDs are inherently more risky than binary options and forex as they have an unlimited downside risk and can sometimes be taken out on leverage. Traders who understand the risk and know how to place solid stop losses can indeed profit from them.
However, for those traders who would prefer to take a directional “bet” with defined maximum losses, then binary options may indeed be for them. Binary Option traders can also enter trades without stops in place as the loss is limited.
Is there an Alternative?
For those traders who would like to trade an instrument that has the entry / exit and leveraged benefits of a CFD with the maximum loss benefit of a binary option, a digital contract could be a good alternative.
These instruments also have an asymmetric payoff but the trader can choose a number of different strike rates. This means that the payoff for some of these trades can vary from 50% to 2,000% depending on the initial entry price of the contract.
Even though they are option like instruments, the trader can also exit the trade prior to expiry of the contract at a profit. This could be good for those traders who would like to lock in any potential gains.
Lastly, like binary options, the maximum loss on a digital contract is always defined and is equal to the initial investment that the trader laid out to enter the contract.